Tuberculosis
Since 2000, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and partners have saved more than 79 million lives globally.
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers. Despite being preventable, treatable, and curable, this ancient disease continues to kill more people each year than HIV and malaria combined.
USAID leads the U.S. Government’s global TB efforts. As the largest bilateral TB donor, USAID has invested $4.7 billion dollars to combat TB since 2000. Guided by USAID's Global TB Strategy 2023-2030, and in cooperation with Ministries of Health, USAID provides bilateral assistance in 24 countries with high burdens of TB.
USAID’S GLOBAL TB STRATEGY, 2023-2030
Through the Agency’s Global TB Strategy 2023-2030, USAID works with partners in the Agency’s 24 priority TB countries to achieve the global targets through activities categorized under the strategic objectives of Reach, Cure, Prevent, Innovate, and Sustain. In USAID’s 24 TB priority countries, the strategy aims to reduce TB incidence by 35% and TB mortality by 52% by 2030 with:

A FOCUS ON RESULTS
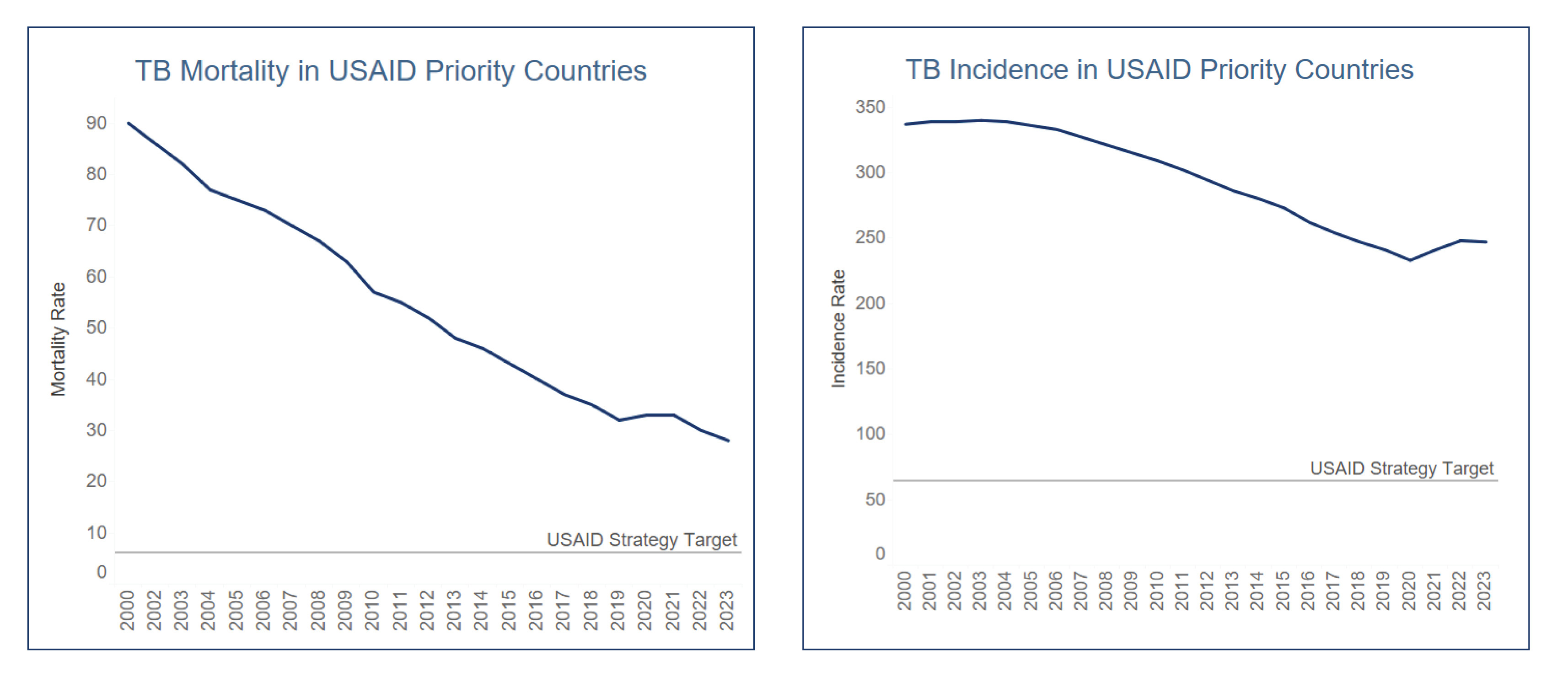
In 2023, TB mortality in USAID’s 24 TB priority countries decreased by eight percent, compared to the 2019 baseline, before the COVID-19 pandemic.Conversely, the estimated TB incidence increased by eight percent from the 2019 baseline, which is indicative of the residual impact of continuing to identify more people with TB missed during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the rate of this increase has been slowing over the last three years.
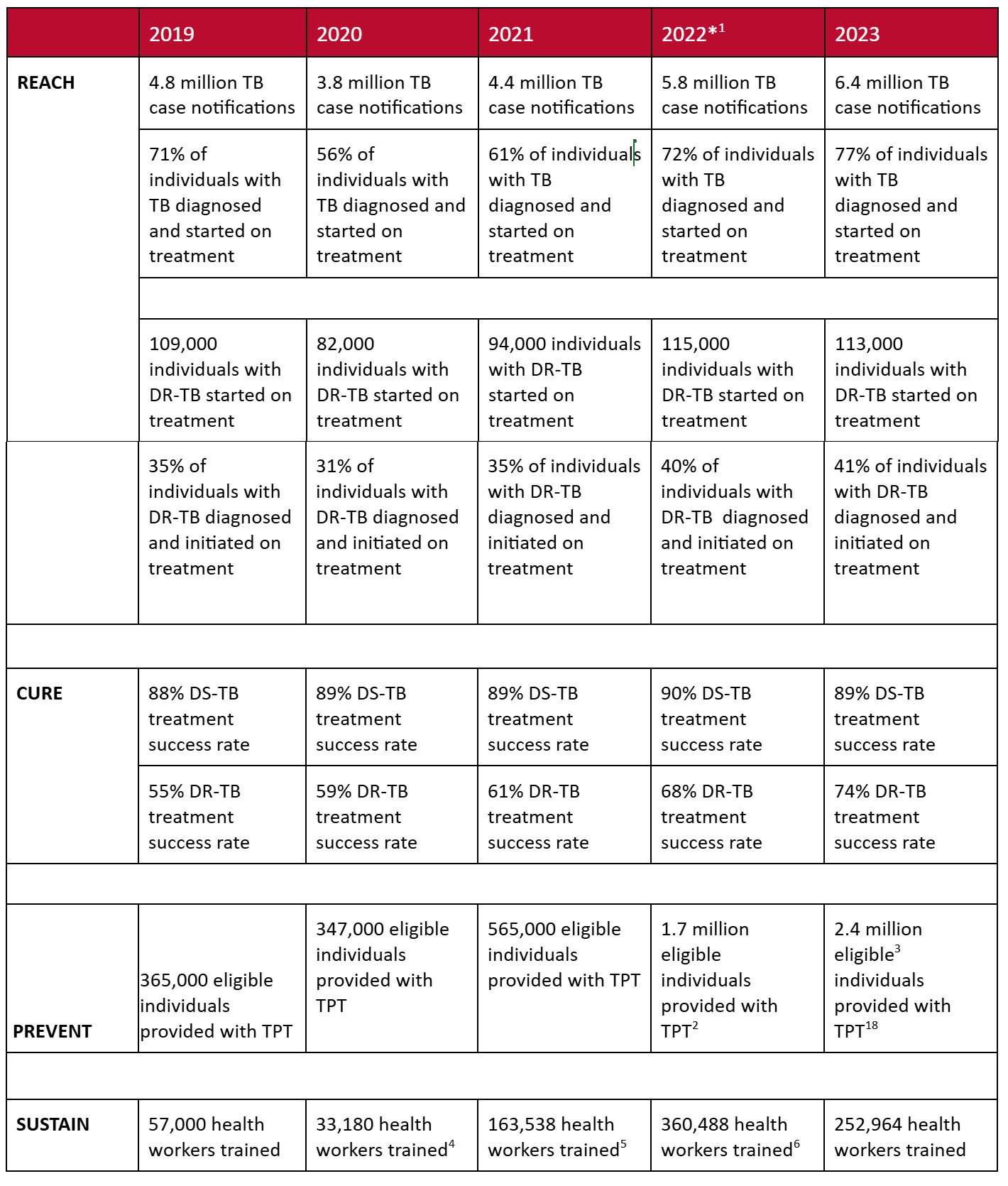
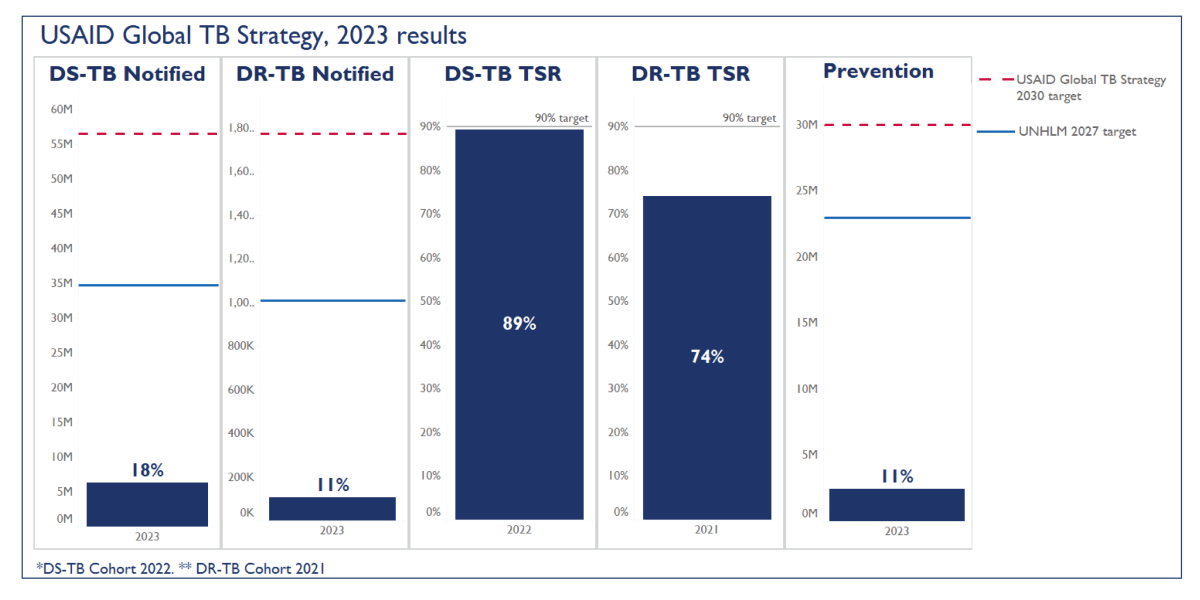
For USAID-supported countries, 2023 represents the first year of implementing and reporting on the USAID Global TB Strategy, 2023-2030 results framework and the UNHLM 2027 targets, which are aligned. While the TSRs for both DS-TB and DR-TB remain high, progress on reaching the DR-TB case notification and prevention targets requires accelerated efforts. As indicated in the USAID Priority Country Statistics 2019-2023 table (see page 11), the number of individuals with DR-TB who were diagnosed and started on treatment declined slightly in 2023 due to results reported by a few countries. USAID is working with these countries to address factors related to delays in DR-TB treatment initiation.
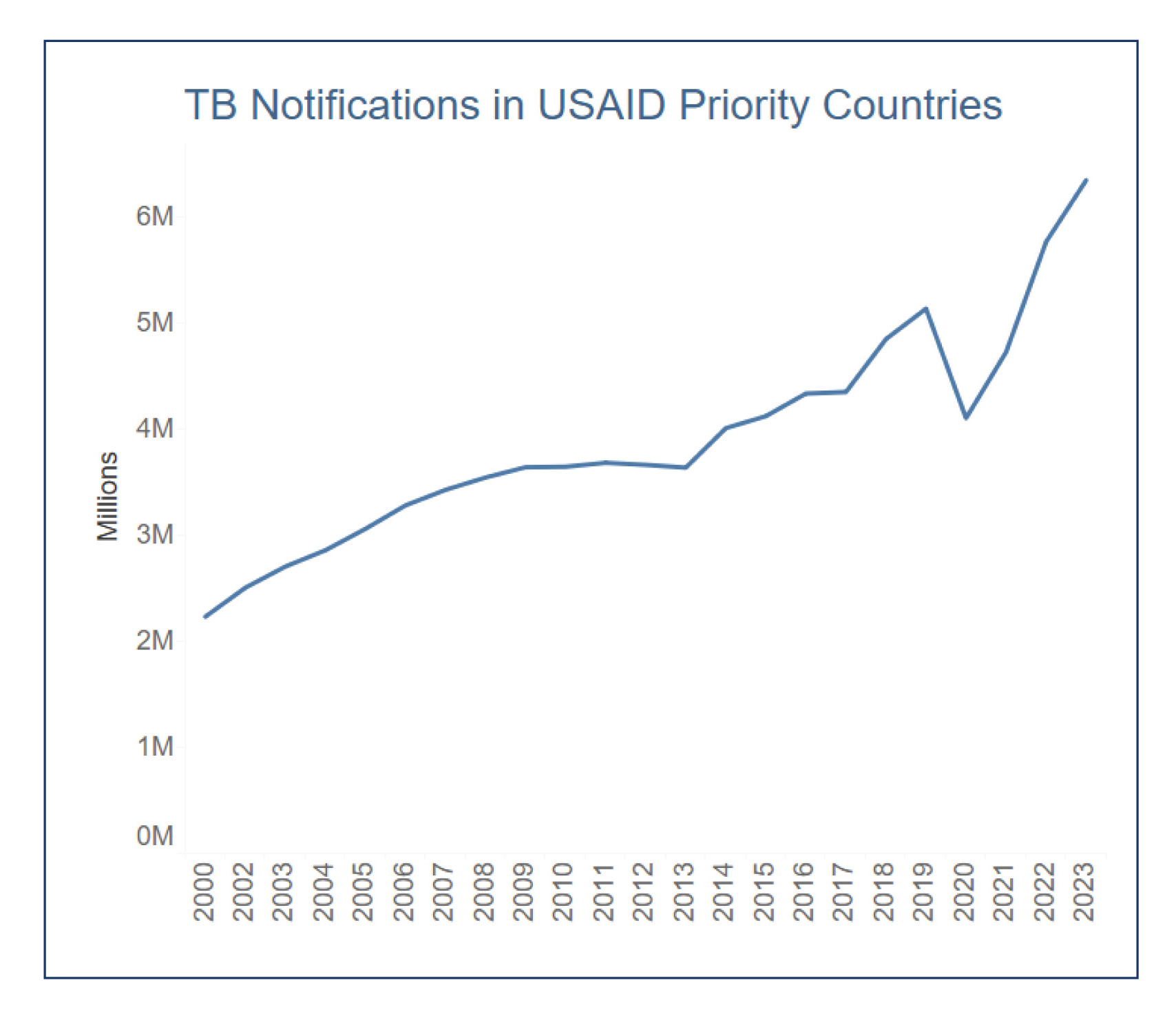
Importantly, TB case notifications in USAID’s TB priority countries increased in 2023 by 10 percent compared to 2022 (5,773,695 versus 6,354,096 )—a 24 percent increase in comparison to 2019 pre-COVID-19 levels.